How to Determine if You Have Acne-Prone Skin?
By paying attention to these signs and taking proactive steps to care for your skin, you can effectively manage acne-prone skin and achieve a clearer, healthier complexion.
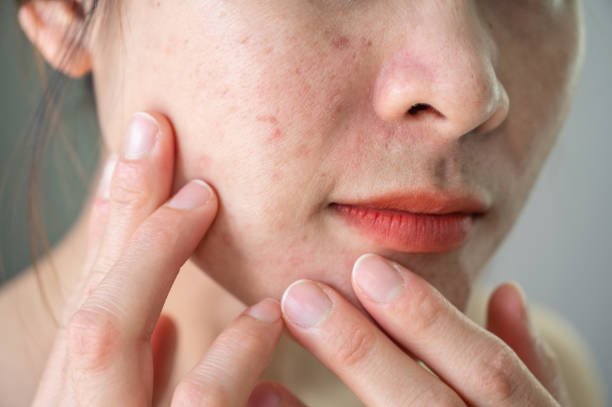
Acne is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, leading to the formation of pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads. Isotretinoin 20mg will help in curing acne. While acne can occur on any skin type, some people are more prone to developing it than others.
Signs:
If you're wondering whether you have acne-prone skin, here are some signs to look out for:
- Frequent Breakouts: One of the key indicators of acne-prone skin is the presence of frequent breakouts. If you find yourself regularly dealing with pimples and other blemishes, it's likely that you have acne-prone skin.
- Oily Skin: People with acne-prone skin often have an oily complexion. This is because their skin produces excess sebum, which can clog pores and lead to acne breakouts.
- Clogged Pores: Another sign of acne-prone skin is the presence of clogged pores. You may notice that your pores appear larger or more noticeable, and you may also experience blackheads and whiteheads.
- Sensitive Skin: Acne-prone skin is often sensitive and can react negatively to harsh ingredients or products. If your skin tends to become red, irritated, or inflamed easily, it may be acne-prone.
- History of Acne: If you have a history of acne, especially if it runs in your family, you are more likely to have acne-prone skin.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Hormonal imbalances can contribute to acne breakouts. If you notice that your acne tends to flare up around certain times of the month, it may be due to hormonal changes.
- Diet and Lifestyle Factors: Your diet and lifestyle can also play a role in determining whether you have acne-prone skin. A diet high in sugar and dairy products, as well as factors like stress and lack of sleep, can all contribute to acne breakouts.
Symptoms:
- Pimples: The most common symptom of acne-prone skin is the presence of pimples. These can range from small, red bumps to larger, pus-filled cysts.
- Blackheads and Whiteheads: Clogged pores can also lead to the formation of blackheads (open comedones) and whiteheads (closed comedones).
- Inflammation: Acne-prone skin is often inflamed, with redness and swelling around the affected areas.
- Oily Skin: People with acne-prone skin often have an oily complexion, as their skin produces excess sebum.
- Scarring: In severe cases, acne breakouts can lead to scarring, which may be temporary or permanent.
- Tenderness: Acne lesions can be tender to the touch, especially in cases of inflamed or cystic acne.
If you suspect that you have acne-prone skin, it's important to take steps to care for your skin properly. This includes using gentle, non-comedogenic skincare products, avoiding harsh ingredients, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. If your acne is severe or persistent, it's best to consult with a dermatologist who can recommend a treatment plan tailored to your specific skin type and concerns.
Treatment for Acne-Prone Skin
Acne-prone skin can be frustrating to deal with, but with the right treatment, you can effectively manage breakouts and improve the overall health of your skin. Here are some common treatments for acne-prone skin:
Topical Treatments:
- Benzoyl Peroxide: This ingredient helps to kill acne-causing bacteria and reduce inflammation. It is available over-the-counter in various strengths.
- Salicylic Acid: Salicylic acid helps to unclog pores and exfoliate the skin, preventing new acne breakouts. It is commonly found in acne cleansers, toners, and spot treatments.
- Retinoids: Prescription retinoids, such as tretinoin, adapalene, and tazarotene, help to unclog pores, reduce inflammation, and promote skin cell turnover. They are highly effective for treating acne but can be irritating to the skin, so they should be used with caution.
- Topical Antibiotics: Antibiotics, such as clindamycin and erythromycin, can help to reduce acne-causing bacteria on the skin and decrease inflammation. They are often used in combination with other acne treatments.
Oral Medications:
- Oral Antibiotics: In cases of moderate to severe acne, oral antibiotics, such as doxycycline, minocycline, or tetracycline, may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and kill acne-causing bacteria.
- Oral Contraceptives: For women, oral contraceptives that contain estrogen and progestin can help to regulate hormone levels and reduce acne breakouts.
- Isotretinoin: Isotretinoin 40 mg, also known as Accutane, is a powerful oral medication that is used to treat severe acne. It works by reducing sebum production, unclogging pores, and reducing inflammation. However, it can have serious side effects and is usually reserved for severe cases of acne that have not responded to other treatments.
Lifestyle Changes:
- Gentle Cleansing: Use a gentle cleanser twice a day to remove excess oil, dirt, and dead skin cells from the skin. Avoid harsh scrubbing, as this can irritate the skin and worsen acne.
- Moisturizing: Use a lightweight, non-comedogenic moisturizer to keep the skin hydrated without clogging pores.
- Sun Protection: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to protect the skin from UV damage, which can worsen acne and lead to hyperpigmentation.
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid foods high in sugars and refined carbohydrates, as these can contribute to acne breakouts.
- Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises, as stress can worsen acne.
Professional Treatments:
- Chemical Peels: Chemical peels use a chemical solution to exfoliate the skin, unclog pores, and improve the appearance of acne scars.
- Microdermabrasion: Microdermabrasion uses a device to gently exfoliate the outer layer of the skin, helping to unclog pores and reduce acne breakouts.
- Laser Therapy: Laser therapy uses focused light energy to target and destroy acne-causing bacteria, reduce inflammation, and promote skin healing.
It's important to consult with a dermatologist before starting any new acne treatment regimen, as they can help determine the best course of treatment for your individual skin type and concerns. With the right treatment plan, you can effectively manage acne-prone skin and achieve a clearer, healthier complexion.
By paying attention to these signs and taking proactive steps to care for your skin, you can effectively manage acne-prone skin and achieve a clearer, healthier complexion.
What's Your Reaction?











![Wireless Connectivity Software Market Size, Share | Statistics [2032]](https://handyclassified.com/uploads/images/202404/image_100x75_661f3be896033.jpg)



