Understanding the Role of Wireless Modules in IoT
Explore the vital role of wireless modules in IoT projects, uncovering their features, benefits, and real-world applications across industries. Discover why these modules are essential for seamless connectivity and data exchange in the IoT ecosystem.
Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) represents a significant leap in how devices communicate and interact with each other and with us. Central to this revolution are wireless modules, the unsung heroes that enable seamless connectivity and data exchange.
As IoT continues to infiltrate various sectors, understanding the role and benefits of wireless modules becomes crucial for leveraging their full potential.
This blog post delves into the essential functions of wireless modules in IoT, their features, benefits, and real-world applications, shedding light on why they are indispensable in modern trendy IoT projects.
Role of Wireless Modules in IoT Projects
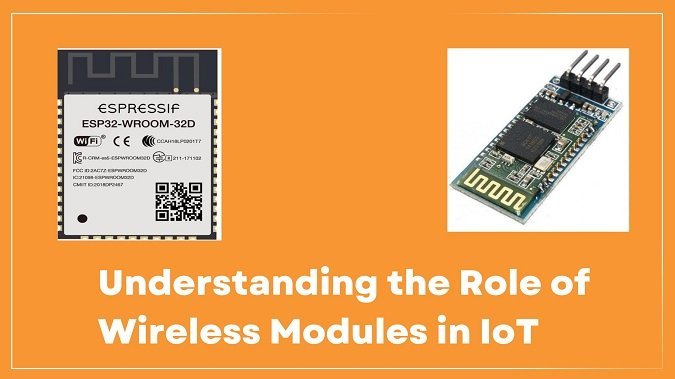
Wireless modules are integral components in IoT architecture, providing the necessary communication link between devices and networks. These modules come equipped with various wireless communication standards like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and cellular connectivity, each suited for different IoT applications. The role of these modules can be categorized into several key functions:
Data Transmission:
It enable the transmission of data between devices and cloud platforms. This transmission can be direct or through gateways that aggregate data from multiple devices.
Network Connectivity:
They facilitate the connectivity of IoT devices to local networks and the internet, ensuring devices remain accessible and manageable remotely.
Interoperability:
By supporting multiple communication protocols, wireless modules allow diverse devices to communicate within an IoT ecosystem, promoting interoperability and integration.
Energy Management:
Many wireless modules are designed to be energy-efficient, a critical feature for battery-powered IoT devices that need to operate over extended periods without frequent recharging.
Features and Benefits of Using Wireless Modules
The adoption of wireless modules in IoT projects brings numerous advantages, attributed to their versatile features:
Flexibility and Scalability:
Wireless modules allow IoT networks to be easily scalable. New devices can be added without extensive wiring or infrastructure changes, promoting flexible network expansion.
Cost-Effectiveness:
By eliminating the need for physical connections, wireless modules reduce installation and maintenance costs. They also lower operational expenses by minimizing power consumption.
Ease of Deployment:
Wireless modules simplify the deployment of IoT solutions, enabling quick and straightforward installation. This is particularly beneficial in remote or hard-to-reach areas where wired connections are impractical.
Robust Security:
Modern wireless modules incorporate advanced security features, such as encryption and authentication protocols, to protect data integrity and prevent unauthorized access.
Improved Data Accessibility:
With wireless modules, data can be accessed and monitored in real-time from any location, facilitating timely decision-making and proactive management of IoT systems.
Real-World Applications of Wireless Modules in IoT
Wireless modules find applications across a myriad of industries, demonstrating their versatility and indispensability:
Smart Homes:
Wireless modules enable smart home devices such as thermostats, security cameras, and lighting systems to communicate and be controlled remotely via smartphones or voice assistants, enhancing convenience and energy efficiency.
Healthcare:
In healthcare, wireless modules are crucial in wearable devices and remote monitoring systems, allowing continuous patient monitoring and real-time data transmission to healthcare providers, improving patient care and outcomes.
Agriculture:
IoT applications in agriculture rely on wireless modules for precision farming. Sensors distributed across fields collect data on soil moisture, temperature, and crop health, transmitting it to cloud platforms for analysis, optimizing irrigation and fertilization processes.
Industrial Automation:
In manufacturing, wireless modules facilitate the automation of production lines. They connect sensors and machinery, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and enhancing productivity.
Transportation and Logistics:
Wireless modules in IoT are transforming transportation by enabling smart fleet management systems. They provide real-time tracking of vehicles, monitor engine health, and optimize routes, enhancing efficiency and reducing operational costs.
Environmental Monitoring:
Environmental monitoring systems equipped with these modules can collect data on air quality, water levels, and weather conditions, providing critical information for disaster management and environmental conservation efforts.
Final Thoughts
Wireless modules are the backbone of IoT, enabling the connectivity and communication that define the modern landscape of smart devices and systems. Their role in data transmission, network connectivity, and interoperability is fundamental to the success of IoT projects across various industries.
The features and benefits they offer, from cost-effectiveness to robust security, make them a preferred choice for implementing efficient and scalable IoT solutions. As IoT continues to evolve, the significance of wireless modules will only grow, driving innovation and enhancing the quality of life through smarter, more connected environments.
What's Your Reaction?











![Wireless Connectivity Software Market Size, Share | Statistics [2032]](https://handyclassified.com/uploads/images/202404/image_100x75_661f3be896033.jpg)


