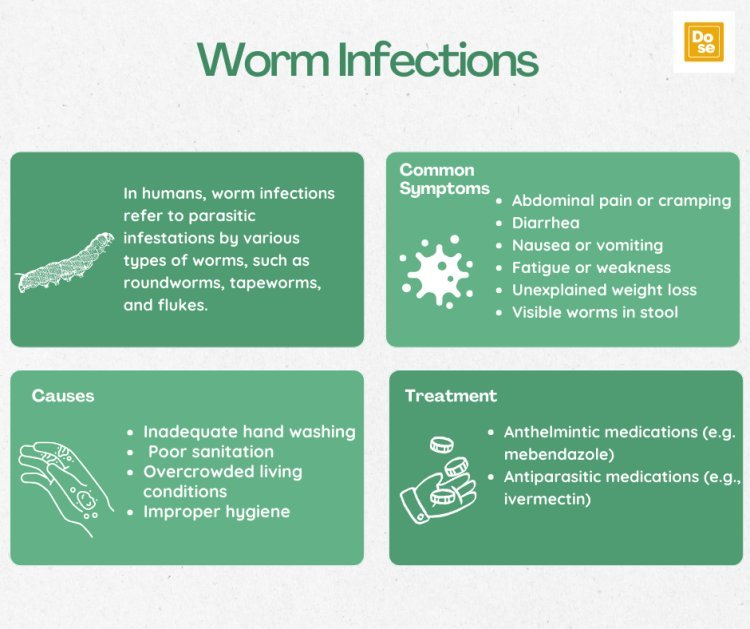
Worm infections, also known as helminthiasis, are a common health issue worldwide, especially in areas with poor sanitation and limited access to clean water. These infections can be caused by different types of worms, including roundworms, tapeworms, and hookworms. While they are often treatable, prevention is key to reducing the risk of infection. In this blog post, we will discuss the treatments available for worm infections and effective prevention strategies.
Treatments for Worm Infections
-
Medications: The primary treatment for worm infections is the use of anthelmintic medications. These drugs are designed to kill the worms in the body. Commonly used medications include nitazoxanide 500 mg, mebendazole, and praziquantel. The choice of medication depends on the type of worm causing the infection.
-
Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be required to remove the worms from the body. This is more common with tapeworm infections, where the worms may form cysts in tissues such as the liver or lungs.
-
Antibiotics: Antibiotics may be prescribed if a bacterial infection is present alongside the worm infection. This is common in cases of tapeworm infections.
-
Supportive Care: In addition to medication, supportive care may be needed to manage symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Rehydration and nutritional support may also be necessary, especially in severe cases.
Prevention Strategies for Worm Infections
-
Hand Hygiene: Practicing good hand hygiene, such as washing hands with soap and water before eating and after using the toilet, can help prevent worm infections.
-
Sanitation: Ensuring access to clean water and proper sanitation facilities can reduce the risk of worm infections. This includes using safe drinking water sources and proper disposal of human waste.
-
Food Safety: Properly cooking meat and fish can kill any parasites that may be present. It is also important to wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly before consuming them.
-
Avoiding Contaminated Soil: Avoiding contact with soil that may be contaminated with human or animal feces can reduce the risk of worm infections. This is especially important in areas where worm infections are common.
-
Treatment of Infected Individuals: Treating infected individuals promptly can help prevent the spread of worms to others. It is important to follow the prescribed treatment nitazoxanide 200 mg regimen carefully to ensure the infection is fully cleared.
-
Regular Deworming: In areas where worm infections are common, regular deworming programs may be implemented to reduce the overall burden of infection in the community.
Conclusion
Worm infections are a significant health issue, especially in developing countries. While they are often treatable, prevention is key to reducing the risk of infection. Practicing good hand hygiene, ensuring access to clean water and sanitation facilities, and avoiding contact with contaminated soil are important preventive measures. In cases where infection does occur, prompt treatment with anthelmintic medications can help clear the infection. By following these strategies, we can work towards reducing the burden of worm infections worldwide.











![Wireless Connectivity Software Market Size, Share | Statistics [2032]](https://handyclassified.com/uploads/images/202404/image_100x75_661f3be896033.jpg)




